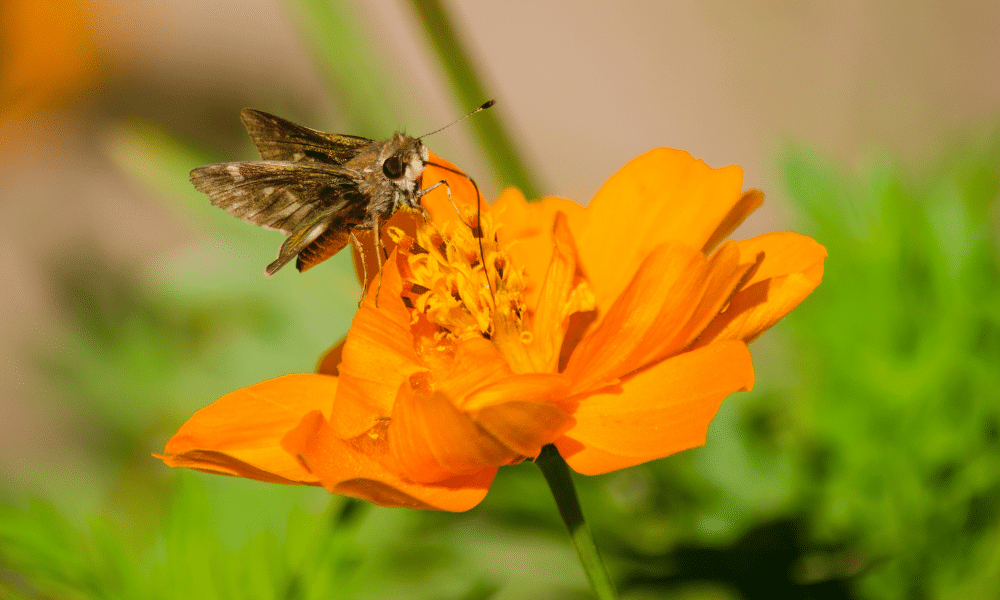
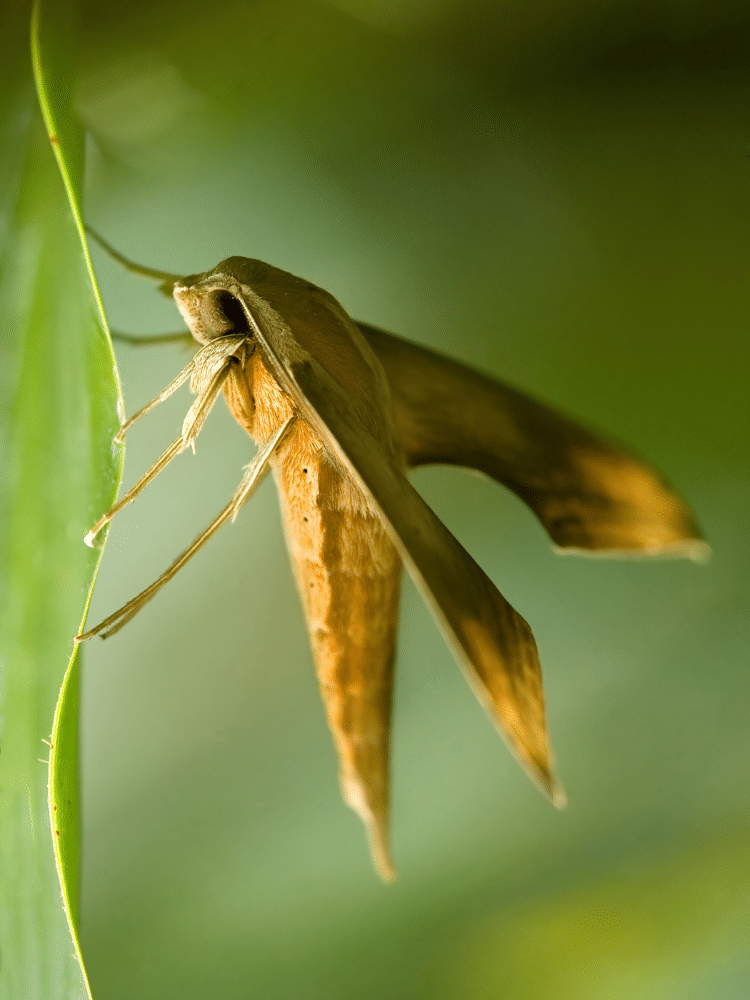
If you’re remotely interested in insects and wildlife, then you probably know what most of them eat. You know that caterpillars munch away at cabbage leaves. You know that bees collect pollen. But what do moths eat? Do they even eat at all?
Moths primarily feed on nectar from flowers, sap from trees, and other sugary substances. Some species also consume pollen.
Our Full List of What Moths Eat
With thousands of different moth types in the wild, it should go without saying that their diets can vary from species to species, and what they require to survive will always change. But this is a full list of what most moths will eat when they are adults:
- Nectar
Adult moths commonly feed on nectar from flowers, which provides them with essential carbohydrates and energy. This is why you’ll often see moths on high-nectar plants during the evening – especially those with a flat flowerhead. - Sap
Some moth species feed on sap from trees. Sap tends to be incredibly nutrient-rich, so if a moth can consume sap, it will. - Honeydew
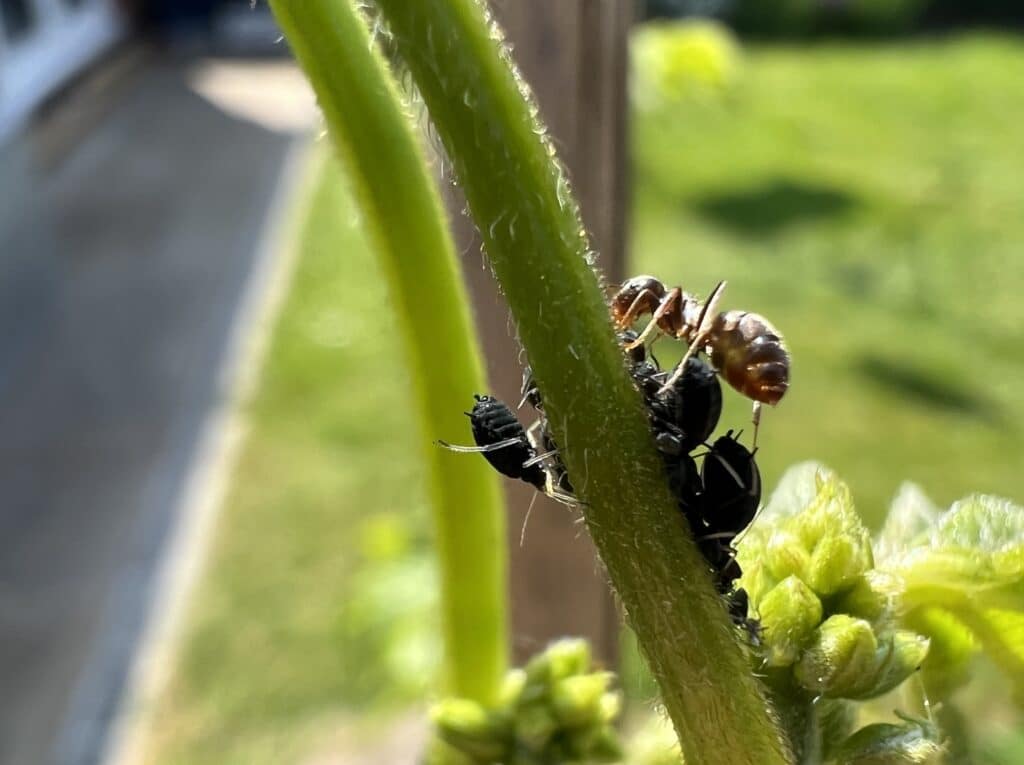
Moths may also consume honeydew, a sweet substance excreted by sap-feeding insects like aphids, as an additional source of carbohydrates. They will have to fight off other insects, such as ants, for it, though. It’s popular stuff!

- Pollen
Certain moth species visit flowers to collect pollen grains, which provide protein. Generally, however, if a moth is on a flower, it is for nectar and not pollen. - Rotting Fruit
Some moths are attracted to rotting or fermenting fruits, where they feed on juices and decaying matter. - Animal Droppings
Yes, there are moths which are attracted to animal droppings and feed on them to obtain nutrients and minerals. - Carrion
Certain moth species, known unimaginatively as carrion moths, are attracted to decaying animal carcasses, feeding on the decomposing tissue. - Fungi
Some moths have been observed feeding on specific types of fungi, potentially providing them with nutrients and aiding in spore dispersal. - Algae
Moths found in aquatic or wetland environments may consume algae as a food source. - Clothes
Clothes moths will feed on natural fibres like wool, fur, feather, and silk, causing damage to clothing and textiles.
Yes, some species of moths, specifically clothes moths, feed on natural fibres found in many clothes. This can lead to holes appearing in your clothing, unfortunately.
While adult moths primarily feed on nectar and sap, moth larvae (caterpillars) can eat plants, consuming leaves, flowers, or plant matter as their primary food source.
Adult moths do not eat bugs. But certain moth larvae species feed on other insects and bugs as part of their diet, acting as natural predators in ecosystems, including tiger moths and hawkmoths.
How Do Moths Feed?
A moth feeds through a process known as proboscis feeding. The proboscis is a long, tubular mouthpart used by the moth to access food sources such as nectar or sap.
When a moth approaches a suitable food source, it extends its proboscis to reach the desired liquid.
The proboscis comprises two halves, known as galeae, which are held together to form a tube-like structure. The galeae are covered in tiny sensory hairs that help the moth locate the food source.
Once the proboscis makes contact with the liquid, the moth begins a process called capillary action.
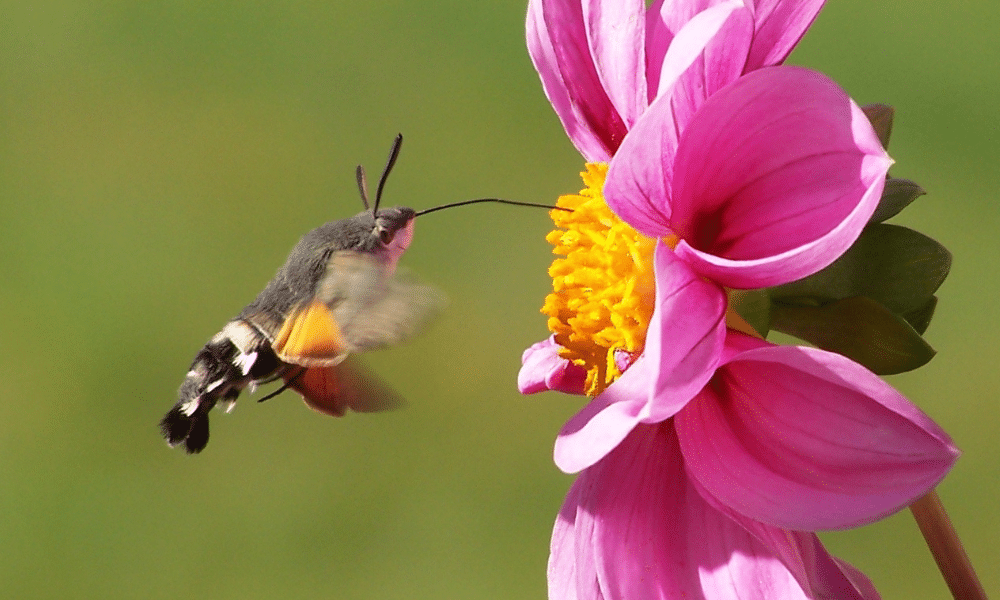
The liquid is drawn up the proboscis through capillary action by the combined forces of adhesion and cohesion. Adhesion allows the liquid to stick to the surface of the proboscis, while cohesion enables the liquid to stick to itself, creating a continuous column within the proboscis.
The moth then pumps muscles near its head to create pressure, propelling the liquid up the proboscis and into its digestive system.
The liquid passes through a food canal tube, which leads to the moth’s midgut. The food is broken down and digested in the midgut, extracting the necessary nutrients for the moth’s survival.
What Do Moths Drink?
The main thing that moths drink is nectar. It is a sugary fluid produced by flowers and serves as the main source of nutrition for adult moths.
Moths use their proboscis, a long, tubular mouthpart, to access the nectar from the flowers.
When a moth locates a flower with nectar, it extends its proboscis and inserts it into the floral structure. The proboscis acts as a straw, allowing the moth to suck up the nectar.
As the moth drinks the nectar, it provides the necessary carbohydrates and energy for its activities, including flight and reproduction.
In addition to nectar, moths may drink other liquids as supplemental food sources. Some moths extract liquid from rotten fruit, tree sap, aphid honeydew and even animal droppings.